实例介绍

# nanoflann
[](https://travis-ci.org/jlblancoc/nanoflann)
## 1. About
*nanoflann* is a **C 11 [header-only](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Header-only) library** for building KD-Trees of datasets with different topologies: R<sup>2</sup>, R<sup>3</sup> (point clouds), SO(2) and SO(3) (2D and 3D rotation groups). No support for approximate NN is provided. *nanoflann* does not require compiling or installing. You just need to `#include <nanoflann.hpp>` in your code.
This library is a *fork* of the [flann library](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) ([git](https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann)) by Marius Muja and David G. Lowe, and born as a child project of [MRPT](https://www.mrpt.org/). Following the original license terms, *nanoflann* is distributed under the BSD license. Please, for bugs use the issues button or fork and open a pull request.
Cite as:
```
@misc{blanco2014nanoflann,
title = {nanoflann: a {C} header-only fork of {FLANN}, a library for Nearest Neighbor ({NN}) with KD-trees},
author = {Blanco, Jose Luis and Rai, Pranjal Kumar},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann}},
year = {2014}
}
```
### 1.1. Obtaining the code
* Easiest way: clone this GIT repository and take the `include/nanoflann.hpp` file for use where you need it.
* macOS users can install `nanoflann` with [Homebrew](https://brew.sh) with:
```shell
$ brew install brewsci/science/nanoflann
```
or
```shell
$ brew tap brewsci/science
$ brew install nanoflann
```
* Linux users can install it with [Linuxbrew](https://linuxbrew.sh/) with: `brew install homebrew/science/nanoflann`
* List of [**stable releases**](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/releases). Check out the [CHANGELOG](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/master/CHANGELOG.txt)
Although nanoflann itself doesn't have to be compiled, you can build some examples and tests with:
sudo apt-get install build-essential cmake libgtest-dev libeigen3-dev
mkdir build && cd build && cmake ..
make && make test
### 1.2. C API reference
* Browse the [Doxygen documentation](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/).
* **Important note:** If L2 norms are used, notice that search radius and all passed and returned distances are actually *squared distances*.
### 1.3. Code examples
* KD-tree look-up with `kdd_search()` and `radius_search()`: [pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a point cloud dataset: [pointcloud_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a dynamic point cloud dataset: [dynamic_pointcloud_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/dynamic_pointcloud_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a rotation group (SO2): [SO2_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/SO2_adaptor_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a rotation group (SO3): [SO3_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/SO3_adaptor_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a point cloud dataset with an external adaptor class: [pointcloud_adaptor_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_adaptor_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up directly on an `Eigen::Matrix<>`: [matrix_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/matrix_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up directly on `std::vector<std::vector<T> >` or `std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd>`: [vector_of_vectors_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/vector_of_vectors_example.cpp)
* Example with a `Makefile` for usage through `pkg-config` (for example, after doing a "make install" or after installing from Ubuntu repositories): [example_with_pkgconfig/](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/example_with_pkgconfig/)
* Example of how to build an index and save it to disk for later usage: [saveload_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/saveload_example.cpp)
### 1.4. Why a fork?
* **Execution time efficiency**:
* The power of the original `flann` library comes from the possibility of choosing between different ANN algorithms. The cost of this flexibility is the declaration of pure virtual methods which (in some circumstances) impose [run-time penalties](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~gilpin/c%2B%2B/performance.html#virtualfunctions). In `nanoflann` all those virtual methods have been replaced by a combination of the [Curiously Recurring Template Pattern](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curiously_recurring_template_pattern) (CRTP) and inlined methods, which are much faster.
* For `radiusSearch()`, there is no need to make a call to determine the number of points within the radius and then call it again to get the data. By using STL containers for the output data, containers are automatically resized.
* Users can (optionally) set the problem dimensionality at compile-time via a template argument, thus allowing the compiler to fully unroll loops.
* `nanoflann` allows users to provide a precomputed bounding box of the data, if available, to avoid recomputation.
* Indices of data points have been converted from `int` to `size_t`, which removes a limit when handling very large data sets.
* **Memory efficiency**: Instead of making a copy of the entire dataset into a custom `flann`-like matrix before building a KD-tree index, `nanoflann` allows direct access to your data via an **adaptor interface** which must be implemented in your class.
Refer to the examples below or to the C API of [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html) for more info.
### 1.5. What can *nanoflann* do?
* Building KD-trees with a single index (no randomized KD-trees, no approximate searches).
* Fast, thread-safe querying for closest neighbors on KD-trees. The entry points are:
* [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html)`::knnSearch()`
* Finds the `num_closest` nearest neighbors to `query_point[0:dim-1]`. Their indices are stored inside the result object. See an [example usage code](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp#L119).
* [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html)`::radiusSearch()`
* Finds all the neighbors to `query_point[0:dim-1]` within a maximum radius. The output is given as a vector of pairs, of which the first element is a point index and the second the corresponding distance. See an [example usage code](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp#L141).
* [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html)`::radiusSearchCustomCallback()`
* Can be used to receive a callback for each point found in range. This may be more efficient in some situations instead of building a huge vector of pairs with the results.
* Working with 2D and 3D point clouds or N-dimensional data sets.
* Working directly with `Eigen::Matrix<>` classes (matrices and vectors-of-vectors).
* Working with dynamic point clouds without a need to rebuild entire kd-tree index.
* Working with the distance metrics:
* `R^N`: Euclidean spaces:
* `L1` (Manhattan)
* `L2` (**squared** Euclidean norm, favoring SSE2 optimization).
* `L2_Simple` (**squared** Euclidean norm, for low-dimensionality data sets like point clouds).
* `SO(2)`: 2D rotational group
* `metric_SO2`: Absolute angular diference.
* `SO(3)`: 3D rotational group (better suppport to be provided in future releases)
* `metric_SO3`: Inner product between quaternions.
* Saves and load the built indices to disk.
* GUI based support for benchmarking multiple kd-tree libraries namely nanoflann, flann, fastann and libkdtree.
### 1.6. What can't *nanoflann* do?
* Use other distance metrics apart from L1, L2, SO2 and SO3.
* Support for SE(3) groups.
* Only the C interface exists: there is no support for C, MATLAB or Python.
* There is no automatic algorithm configuration (as described in the original Muja & Lowe's paper).
### 1.7. Use in your project via CMake
You can directly drop the `nanoflann.hpp` file in your project. Alternatively,
the CMake standard method is also available:
* Build and "install" nanoflann. Set `CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX` to a proper path
and then execute `make install` (Linux, OSX) or build the `INSTALL`
target (Visual Studio).
* Then, add something like this to the CMake script of your project:
```
# Find nanoflannConfig.cmake:
find_package(nanoflann)
add_executable(my_project test.cpp)
# Make sure the include path is used:
target_link_libraries(my_project nanoflann::nanoflann)
```
------
## 2. Any help choosing the KD-tree parameters?
### 2.1. `KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptorParams::leaf_max_size`
A KD-tree is... well, a tree :-). And as such it has a root node, a set of intermediary nodes and finally, "leaf" nodes which are those without children.
Points (or, properly, point indices) are only stored in leaf nodes. Each leaf contains a list of which points fall within its range.
While building the tree, nodes are recursively divided until the number of points inside is equal or below some threshold. **That is `leaf_max_size`**. While doing queries, the "tree algorithm" ends by selecting leaf nodes, then performing linear search (one-by-one) for the closest point to the query within all those in the leaf.
So, `leaf_max_size` must be set as a **tradeoff**:
* Large values mean that the tree will be built faster (since the tree will be smaller), but each query will be slower (since the linear search in the leaf is to be done over more points).
* Small values will build the tree much slower (there will be many tree nodes), but queries will be faster... up to some point, since the "tree-part" of the search (logarithmic complexity) still has a significant cost.
What number to select really depends on the application and even on the size of the processor cache memory, so ideally you should do some benchmarking for maximizing efficiency.
But to help choosing a good value as a rule of thumb, I provide the following two benchmarks. Each graph represents the tree build (horizontal) and query (vertical) times for different `leaf_max_size` values between 1 and 10K (as 95% uncertainty ellipses, deformed due to the logarithmic scale).
* A 100K point cloud, uniformly distributed (each point has (x,y,z) `float` coordinates):
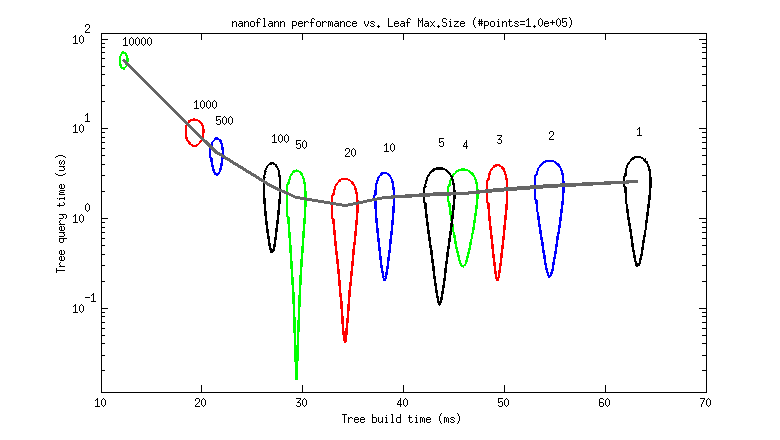
* A ~150K point cloud from a real dataset (`scan_071_points.dat` from the [Freiburg Campus 360 dataset](http://ais.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/projects/datasets/fr360/), each point has (x,y,z) `float` coordinates):
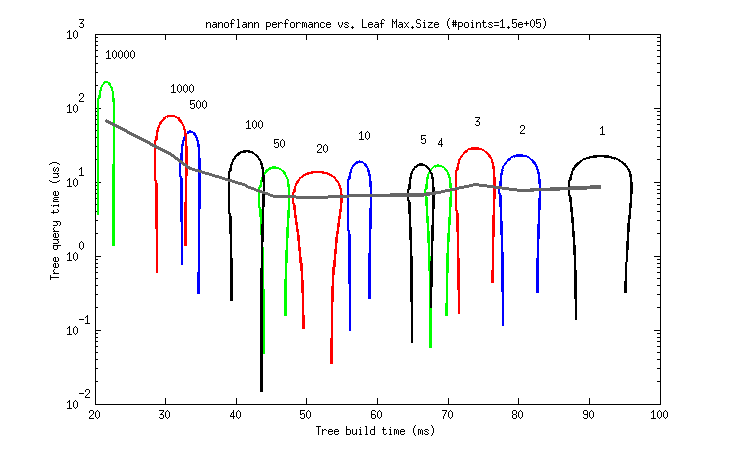
So, it seems that a `leaf_max_size` **between 10 and 50** would be optimum in applications where the cost of queries dominates (e.g. [ICP](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iterative_closest_point])). At present, its default value is 10.
### 2.2. `KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptorParams::checks`
This parameter is really ignored in `nanoflann`, but was kept for backward compatibility with the original FLANN interface. Just ignore it.
-----
## 3. Performance
### 3.1. `nanoflann`: faster and less memory usage
Refer to the "Why a fork?" section above for the main optimization ideas behind `nanoflann`.
Notice that there are no explicit SSE2/SSE3 optimizations in `nanoflann`, but the intensive usage of `inline` and templates in practice turns into automatically SSE-optimized code generated by the compiler.
### 3.2. Benchmark: original `flann` vs `nanoflann`
The most time-consuming part of many point cloud algorithms (like ICP) is querying a KD-Tree for nearest neighbors. This operation is therefore the most time critical.
`nanoflann` provides a ~50% time saving with respect to the original `flann` implementation (times in this chart are in microseconds for each query):
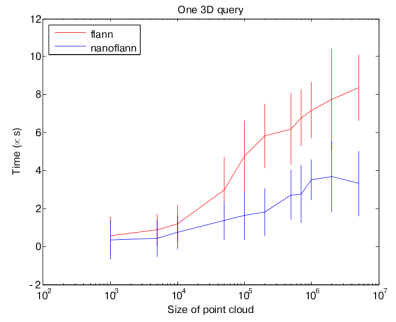
Although most of the gain comes from the queries (due to the large number of them in any typical operation with point clouds), there is also some time saved while building the KD-tree index, due to the templatized-code but also for the avoidance of duplicating the data in an auxiliary matrix (times in the next chart are in milliseconds):
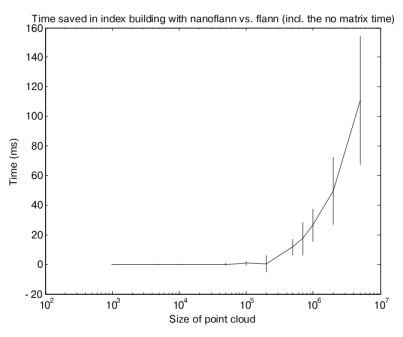
These performance tests are only representative of our testing. If you want to repeat them, read the instructions in [perf-tests](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/tree/master/perf-tests)
----
## 4. Other KD-tree projects
* [FLANN](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) - Marius Muja and David G. Lowe (University of British Columbia).
* [FASTANN](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/software/fastann/) - James Philbin (VGG, University of Oxford).
* [ANN](http://www.cs.umd.edu/~mount/ANN/) - David M. Mount and Sunil Arya (University of Maryland).
* [libkdtree ](https://packages.debian.org/source/sid/libkdtree ) - Martin F. Krafft & others.
<br>
*Note: The project logo is due to [CedarSeed](http://www.iconarchive.com/show/patisserie-icons-by-cedarseed/Flan-icon.html)*
# nanoflann
[](https://travis-ci.org/jlblancoc/nanoflann)
## 1. About
*nanoflann* is a **C 11 [header-only](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Header-only) library** for building KD-Trees of datasets with different topologies: R<sup>2</sup>, R<sup>3</sup> (point clouds), SO(2) and SO(3) (2D and 3D rotation groups). No support for approximate NN is provided. *nanoflann* does not require compiling or installing. You just need to `#include <nanoflann.hpp>` in your code.
This library is a *fork* of the [flann library](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) ([git](https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann)) by Marius Muja and David G. Lowe, and born as a child project of [MRPT](https://www.mrpt.org/). Following the original license terms, *nanoflann* is distributed under the BSD license. Please, for bugs use the issues button or fork and open a pull request.
Cite as:
```
@misc{blanco2014nanoflann,
title = {nanoflann: a {C} header-only fork of {FLANN}, a library for Nearest Neighbor ({NN}) with KD-trees},
author = {Blanco, Jose Luis and Rai, Pranjal Kumar},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann}},
year = {2014}
}
```
### 1.1. Obtaining the code
* Easiest way: clone this GIT repository and take the `include/nanoflann.hpp` file for use where you need it.
* macOS users can install `nanoflann` with [Homebrew](https://brew.sh) with:
```shell
$ brew install brewsci/science/nanoflann
```
or
```shell
$ brew tap brewsci/science
$ brew install nanoflann
```
* Linux users can install it with [Linuxbrew](https://linuxbrew.sh/) with: `brew install homebrew/science/nanoflann`
* List of [**stable releases**](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/releases). Check out the [CHANGELOG](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/master/CHANGELOG.txt)
Although nanoflann itself doesn't have to be compiled, you can build some examples and tests with:
sudo apt-get install build-essential cmake libgtest-dev libeigen3-dev
mkdir build && cd build && cmake ..
make && make test
### 1.2. C API reference
* Browse the [Doxygen documentation](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/).
* **Important note:** If L2 norms are used, notice that search radius and all passed and returned distances are actually *squared distances*.
### 1.3. Code examples
* KD-tree look-up with `kdd_search()` and `radius_search()`: [pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a point cloud dataset: [pointcloud_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a dynamic point cloud dataset: [dynamic_pointcloud_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/dynamic_pointcloud_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a rotation group (SO2): [SO2_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/SO2_adaptor_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a rotation group (SO3): [SO3_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/SO3_adaptor_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up on a point cloud dataset with an external adaptor class: [pointcloud_adaptor_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_adaptor_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up directly on an `Eigen::Matrix<>`: [matrix_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/matrix_example.cpp)
* KD-tree look-up directly on `std::vector<std::vector<T> >` or `std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd>`: [vector_of_vectors_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/vector_of_vectors_example.cpp)
* Example with a `Makefile` for usage through `pkg-config` (for example, after doing a "make install" or after installing from Ubuntu repositories): [example_with_pkgconfig/](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/example_with_pkgconfig/)
* Example of how to build an index and save it to disk for later usage: [saveload_example.cpp](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/saveload_example.cpp)
### 1.4. Why a fork?
* **Execution time efficiency**:
* The power of the original `flann` library comes from the possibility of choosing between different ANN algorithms. The cost of this flexibility is the declaration of pure virtual methods which (in some circumstances) impose [run-time penalties](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~gilpin/c%2B%2B/performance.html#virtualfunctions). In `nanoflann` all those virtual methods have been replaced by a combination of the [Curiously Recurring Template Pattern](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curiously_recurring_template_pattern) (CRTP) and inlined methods, which are much faster.
* For `radiusSearch()`, there is no need to make a call to determine the number of points within the radius and then call it again to get the data. By using STL containers for the output data, containers are automatically resized.
* Users can (optionally) set the problem dimensionality at compile-time via a template argument, thus allowing the compiler to fully unroll loops.
* `nanoflann` allows users to provide a precomputed bounding box of the data, if available, to avoid recomputation.
* Indices of data points have been converted from `int` to `size_t`, which removes a limit when handling very large data sets.
* **Memory efficiency**: Instead of making a copy of the entire dataset into a custom `flann`-like matrix before building a KD-tree index, `nanoflann` allows direct access to your data via an **adaptor interface** which must be implemented in your class.
Refer to the examples below or to the C API of [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html) for more info.
### 1.5. What can *nanoflann* do?
* Building KD-trees with a single index (no randomized KD-trees, no approximate searches).
* Fast, thread-safe querying for closest neighbors on KD-trees. The entry points are:
* [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html)`::knnSearch()`
* Finds the `num_closest` nearest neighbors to `query_point[0:dim-1]`. Their indices are stored inside the result object. See an [example usage code](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp#L119).
* [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html)`::radiusSearch()`
* Finds all the neighbors to `query_point[0:dim-1]` within a maximum radius. The output is given as a vector of pairs, of which the first element is a point index and the second the corresponding distance. See an [example usage code](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/blob/master/examples/pointcloud_kdd_radius.cpp#L141).
* [nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<>](http://jlblancoc.github.io/nanoflann/classnanoflann_1_1KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor.html)`::radiusSearchCustomCallback()`
* Can be used to receive a callback for each point found in range. This may be more efficient in some situations instead of building a huge vector of pairs with the results.
* Working with 2D and 3D point clouds or N-dimensional data sets.
* Working directly with `Eigen::Matrix<>` classes (matrices and vectors-of-vectors).
* Working with dynamic point clouds without a need to rebuild entire kd-tree index.
* Working with the distance metrics:
* `R^N`: Euclidean spaces:
* `L1` (Manhattan)
* `L2` (**squared** Euclidean norm, favoring SSE2 optimization).
* `L2_Simple` (**squared** Euclidean norm, for low-dimensionality data sets like point clouds).
* `SO(2)`: 2D rotational group
* `metric_SO2`: Absolute angular diference.
* `SO(3)`: 3D rotational group (better suppport to be provided in future releases)
* `metric_SO3`: Inner product between quaternions.
* Saves and load the built indices to disk.
* GUI based support for benchmarking multiple kd-tree libraries namely nanoflann, flann, fastann and libkdtree.
### 1.6. What can't *nanoflann* do?
* Use other distance metrics apart from L1, L2, SO2 and SO3.
* Support for SE(3) groups.
* Only the C interface exists: there is no support for C, MATLAB or Python.
* There is no automatic algorithm configuration (as described in the original Muja & Lowe's paper).
### 1.7. Use in your project via CMake
You can directly drop the `nanoflann.hpp` file in your project. Alternatively,
the CMake standard method is also available:
* Build and "install" nanoflann. Set `CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX` to a proper path
and then execute `make install` (Linux, OSX) or build the `INSTALL`
target (Visual Studio).
* Then, add something like this to the CMake script of your project:
```
# Find nanoflannConfig.cmake:
find_package(nanoflann)
add_executable(my_project test.cpp)
# Make sure the include path is used:
target_link_libraries(my_project nanoflann::nanoflann)
```
------
## 2. Any help choosing the KD-tree parameters?
### 2.1. `KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptorParams::leaf_max_size`
A KD-tree is... well, a tree :-). And as such it has a root node, a set of intermediary nodes and finally, "leaf" nodes which are those without children.
Points (or, properly, point indices) are only stored in leaf nodes. Each leaf contains a list of which points fall within its range.
While building the tree, nodes are recursively divided until the number of points inside is equal or below some threshold. **That is `leaf_max_size`**. While doing queries, the "tree algorithm" ends by selecting leaf nodes, then performing linear search (one-by-one) for the closest point to the query within all those in the leaf.
So, `leaf_max_size` must be set as a **tradeoff**:
* Large values mean that the tree will be built faster (since the tree will be smaller), but each query will be slower (since the linear search in the leaf is to be done over more points).
* Small values will build the tree much slower (there will be many tree nodes), but queries will be faster... up to some point, since the "tree-part" of the search (logarithmic complexity) still has a significant cost.
What number to select really depends on the application and even on the size of the processor cache memory, so ideally you should do some benchmarking for maximizing efficiency.
But to help choosing a good value as a rule of thumb, I provide the following two benchmarks. Each graph represents the tree build (horizontal) and query (vertical) times for different `leaf_max_size` values between 1 and 10K (as 95% uncertainty ellipses, deformed due to the logarithmic scale).
* A 100K point cloud, uniformly distributed (each point has (x,y,z) `float` coordinates):

* A ~150K point cloud from a real dataset (`scan_071_points.dat` from the [Freiburg Campus 360 dataset](http://ais.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/projects/datasets/fr360/), each point has (x,y,z) `float` coordinates):

So, it seems that a `leaf_max_size` **between 10 and 50** would be optimum in applications where the cost of queries dominates (e.g. [ICP](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iterative_closest_point])). At present, its default value is 10.
### 2.2. `KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptorParams::checks`
This parameter is really ignored in `nanoflann`, but was kept for backward compatibility with the original FLANN interface. Just ignore it.
-----
## 3. Performance
### 3.1. `nanoflann`: faster and less memory usage
Refer to the "Why a fork?" section above for the main optimization ideas behind `nanoflann`.
Notice that there are no explicit SSE2/SSE3 optimizations in `nanoflann`, but the intensive usage of `inline` and templates in practice turns into automatically SSE-optimized code generated by the compiler.
### 3.2. Benchmark: original `flann` vs `nanoflann`
The most time-consuming part of many point cloud algorithms (like ICP) is querying a KD-Tree for nearest neighbors. This operation is therefore the most time critical.
`nanoflann` provides a ~50% time saving with respect to the original `flann` implementation (times in this chart are in microseconds for each query):

Although most of the gain comes from the queries (due to the large number of them in any typical operation with point clouds), there is also some time saved while building the KD-tree index, due to the templatized-code but also for the avoidance of duplicating the data in an auxiliary matrix (times in the next chart are in milliseconds):

These performance tests are only representative of our testing. If you want to repeat them, read the instructions in [perf-tests](https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann/tree/master/perf-tests)
----
## 4. Other KD-tree projects
* [FLANN](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) - Marius Muja and David G. Lowe (University of British Columbia).
* [FASTANN](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/software/fastann/) - James Philbin (VGG, University of Oxford).
* [ANN](http://www.cs.umd.edu/~mount/ANN/) - David M. Mount and Sunil Arya (University of Maryland).
* [libkdtree ](https://packages.debian.org/source/sid/libkdtree ) - Martin F. Krafft & others.
<br>
*Note: The project logo is due to [CedarSeed](http://www.iconarchive.com/show/patisserie-icons-by-cedarseed/Flan-icon.html)*
好例子网口号:伸出你的我的手 — 分享!
小贴士
感谢您为本站写下的评论,您的评论对其它用户来说具有重要的参考价值,所以请认真填写。
- 类似“顶”、“沙发”之类没有营养的文字,对勤劳贡献的楼主来说是令人沮丧的反馈信息。
- 相信您也不想看到一排文字/表情墙,所以请不要反馈意义不大的重复字符,也请尽量不要纯表情的回复。
- 提问之前请再仔细看一遍楼主的说明,或许是您遗漏了。
- 请勿到处挖坑绊人、招贴广告。既占空间让人厌烦,又没人会搭理,于人于己都无利。
关于好例子网
本站旨在为广大IT学习爱好者提供一个非营利性互相学习交流分享平台。本站所有资源都可以被免费获取学习研究。本站资源来自网友分享,对搜索内容的合法性不具有预见性、识别性、控制性,仅供学习研究,请务必在下载后24小时内给予删除,不得用于其他任何用途,否则后果自负。基于互联网的特殊性,平台无法对用户传输的作品、信息、内容的权属或合法性、安全性、合规性、真实性、科学性、完整权、有效性等进行实质审查;无论平台是否已进行审查,用户均应自行承担因其传输的作品、信息、内容而可能或已经产生的侵权或权属纠纷等法律责任。本站所有资源不代表本站的观点或立场,基于网友分享,根据中国法律《信息网络传播权保护条例》第二十二与二十三条之规定,若资源存在侵权或相关问题请联系本站客服人员,点此联系我们。关于更多版权及免责申明参见 版权及免责申明



网友评论
我要评论