实例介绍
【实例简介】Solving Mathematical Analysis with Matlab Mathcad Mathematica and Maple
采用Matlab、Mathcad、Mathematica和Maple软件进行数学分析求解
【实例截图】












【核心代码】
Contents
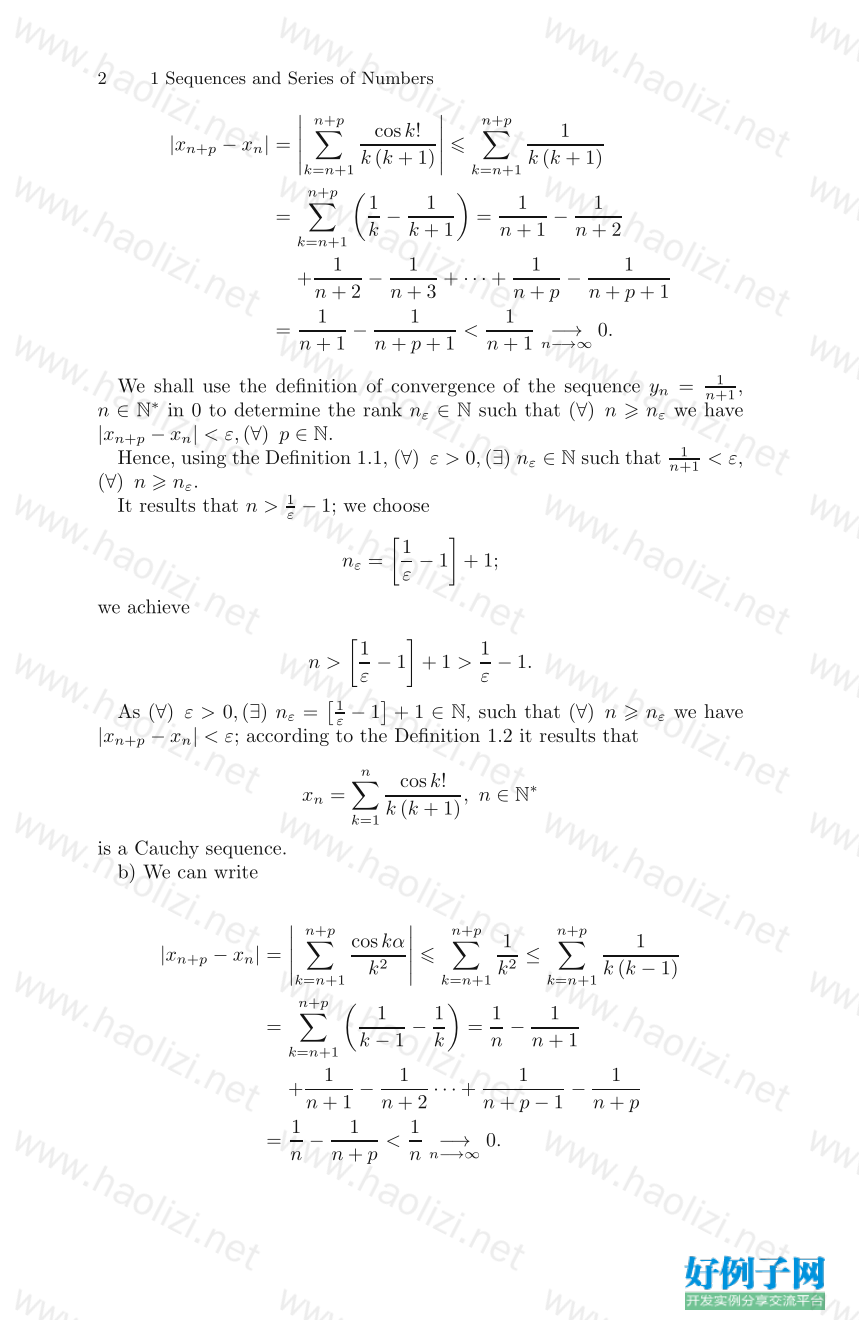
1 Sequences and Series of Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.1 Cauchy Sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2 Fundamental Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2.1 Convergent Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2.1.1 Cauchy’s Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.2.2 Divergent Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.2.3 Operations on Convergent Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.3 Tests for Convergence of Alternating Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.4 Tests of Convergence and Divergence of Positive Series . . . . 16
1.4.1 The Comparison Test I. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
1.4.2 The Root Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1.4.3 The Ratio Test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.4.4 The Raabe’s and Duhamel’s Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.4.5 The Comparison Test II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.4.6 The Comparison Test III . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
1.5 Absolutely Convergent and Semi-convergent Series. . . . . . . . 31
1.6 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2 Power Series. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2.1 Region of Convergence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2.2 Taylor and Mac Laurin Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
2.2.1 Expanding a Function in a Power Series . . . . . . . . . . . 49
2.3 Sum of a Power Series. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
2.4 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
XII Contents
3 Differentiation Theory of the Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3.1 Partial Derivatives and Differentiable Functions
of Several Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3.1.1 Partial Derivatives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3.1.2 The Total Differential of a Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
3.1.3 Applying the Total Differential of a Function
to Approximate Calculations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
3.1.4 The Functional Determinant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
3.1.5 Homogeneous Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
3.2 Derivation and Differentiation of Composite Functions
of Several Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
3.3 Change of Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
3.4 Taylor’s Formula for Functions of Two Variables . . . . . . . . . 126
3.5 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
4 Fundamentals of Field Theory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
4.1 Derivative in a Given Direction of a Function . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
4.2 Differential Operators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
4.3 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
5 Implicit Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
5.1 Derivative of Implicit Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
5.2 Differentiation of Implicit Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
5.3 Systems of Implicit Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
5.4 Functional Dependence. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
5.5 Extreme Value of a Function of Several Variables
Conditional Extremum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
5.6 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
6 Terminology about Integral Calculus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
6.1 Indefinite Integrals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
6.1.1 Integrals of Rational Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
6.1.2 Reducible Integrals to Integrals of Rational
Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
6.1.2.1 Integrating Trigonometric Functions. . . . . . . 251
6.1.2.2 Integrating Certain Irrational Functions . . . 252
6.2 Some Applications of the Definite Integrals in Geometry
and Physics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
6.2.1 The Area under a Curve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
6.2.2 The Area between by Two Curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
6.2.3 Arc Length of a Curve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
6.2.4 Area of a Surface of Revolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
6.2.5 Volumes of Solids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
6.2.6 Centre of Gravity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
Contents XIII
6.3 Improper Integrals.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
6.3.1 Integrals of Unbounded Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
6.3.2 Integrals with Infinite Limits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
6.3.3 The Comparison Criterion for the Integrals . . . . . . . . 293
6.4 Parameter Integrals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
6.5 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
7 Equations and Systems of Linear Ordinary
Differential Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
7.1 Successive Approximation Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
7.2 First Order Differential Equations Solvable
by Quadratures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
7.2.1 First Order Differential Equations with Separable
Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322
7.2.2 First Order Homogeneous Differential Equations . . . 324
7.2.3 Equations with Reduce to Homogeneous
Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
7.2.4 First Order Linear Differential Equations . . . . . . . . . . 330
7.2.5 Exact Differential Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
7.2.6 Bernoulli’s Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
7.2.7 Riccati’s Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
7.2.8 Lagrange’s Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
7.2.9 Clairaut’s Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
7.3 Higher Order Differential Equations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
7.3.1 Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations
with Constant Coefficients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
7.3.2 Non-homogeneous Linear Differential Equations
with Constant Coefficients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
7.3.2.1 The Method of Variation of Constants. . . . . 357
7.3.2.2 The Method of the Undetermined
Coefficients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
7.3.3 Euler’s Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
7.3.4 Homogeneous Systems of Differential Equations
with Constant Coefficients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
7.3.5 Method of Characteristic Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
7.3.6 Elimination Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
7.4 Non-homogeneous Systems of Differential Equations
with Constant Coefficients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
7.5 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
8 Line and Double Integral Calculus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
8.1 Line Integrals of the First Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
8.1.1 Applications of Line Integral of the First Type . . . . . 396
8.2 Line Integrals of the Second Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
8.3 Calculus Way of the Double Integrals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
XIV Contents
8.4 Applications of the Double Integral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
8.4.1 Computing Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
8.4.2 Mass of a Plane Plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 431
8.4.3 Coordinates the Centre of Gravity of a Plane
Plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
8.4.4 Moments of Inertia of a Plane Plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 436
8.4.5 Computing Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
8.5 Change of Variables in Double Integrals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
8.5.1 Change of Variables in Polar Coordinates. . . . . . . . . . 441
8.5.2 Change of Variables in Generalized Polar
Coordinates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445
8.6 Riemann-Green Formula . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
8.7 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
9 Triple and Surface Integral Calculus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 475
9.1 Calculus Way of the Triple Integrals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 475
9.2 Change of Variables in Triple Integrals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
9.2.1 Change of Variables in Spherical Coordinates . . . . . . 477
9.2.2 Change of Variables in Cylindrical Coordinates. . . . . 480
9.3 Applications of the Triple Integrals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
9.3.1 Mass of a Solid. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
9.3.2 Volume of a Solid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
9.3.3 Centre of Gravity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 499
9.3.4 Moments of Inertia . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
9.4 Surface Integral of the First Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
9.5 Surface Integral of the Second Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
9.5.1 Flux of a Vector Field. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 524
9.5.2 Gauss- Ostrogradski Formula . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 529
9.5.3 Stokes Formula . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
9.6 Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 573
List of Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 577
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 579
1
Sequences and Series of N
Solving Mathematical Analysis with Matlab Mathcad Mathematica and Maple
小贴士
感谢您为本站写下的评论,您的评论对其它用户来说具有重要的参考价值,所以请认真填写。
- 类似“顶”、“沙发”之类没有营养的文字,对勤劳贡献的楼主来说是令人沮丧的反馈信息。
- 相信您也不想看到一排文字/表情墙,所以请不要反馈意义不大的重复字符,也请尽量不要纯表情的回复。
- 提问之前请再仔细看一遍楼主的说明,或许是您遗漏了。
- 请勿到处挖坑绊人、招贴广告。既占空间让人厌烦,又没人会搭理,于人于己都无利。
关于好例子网
本站旨在为广大IT学习爱好者提供一个非营利性互相学习交流分享平台。本站所有资源都可以被免费获取学习研究。本站资源来自网友分享,对搜索内容的合法性不具有预见性、识别性、控制性,仅供学习研究,请务必在下载后24小时内给予删除,不得用于其他任何用途,否则后果自负。基于互联网的特殊性,平台无法对用户传输的作品、信息、内容的权属或合法性、安全性、合规性、真实性、科学性、完整权、有效性等进行实质审查;无论平台是否已进行审查,用户均应自行承担因其传输的作品、信息、内容而可能或已经产生的侵权或权属纠纷等法律责任。本站所有资源不代表本站的观点或立场,基于网友分享,根据中国法律《信息网络传播权保护条例》第二十二与二十三条之规定,若资源存在侵权或相关问题请联系本站客服人员,点此联系我们。关于更多版权及免责申明参见 版权及免责申明



网友评论
我要评论