实例介绍
【实例简介】
最近在学习数据结构,写了这个小程序。
程序分为两个部分,一个用递归来生成迷宫,另一个是寻路,也是用递归的方法。下面介绍下思路。
递归就是程序调用自身的一个过程,要跳出递归,必须还有一个“出口”,用来停止递归。生成迷宫的递归的出口就是当前位置的上下左右没有空余的格子。
我用PictureBox作为迷宫的格子,将PictureBox存放在数组里:
假如以map[0,0]作为起始点来生成迷宫的话,程序会随机的选择上下左右中的一个方向来走,如果选中的一个方向中的格子没超出数组界限且没有被遍历过,就记录在位置,然后以该位置为起点,再次随机选择上下左右,这样重复下去,最终将整个格子遍历,其过程像一棵树,map[0,0]就是该数的根。
【实例截图】
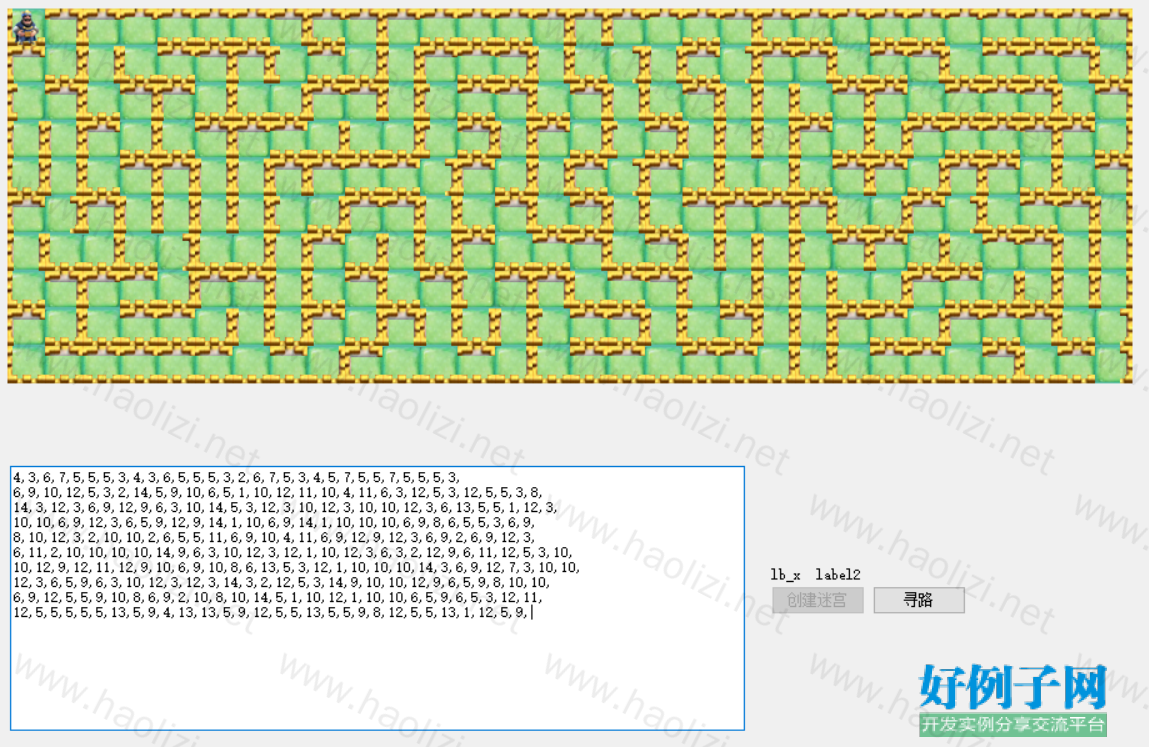
自动寻路

【核心代码】
private void btn_createMap_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
btn_createMap.Enabled = false;
path = new int[height, width];
map = new PictureBox[height, width];
numMap = new int[height, width];
drawCheckerboar();
CreateNumMap((int)height/2, (int)width/2, 0);//在迷宫的中间开始遍历
//CreateNumMap(0, 0, 0);
CreateMap();
}
//绘制pictureBox,数组数据初始化
public void drawCheckerboar()
{
int currentPoint = 0;
int chessLength = 30;
int initX = 10;
int initY = 10;
int _x = initX;
int _y = initY;
PictureBox tmpBox;
for (int x = 0; x < height * width; x )
{
if (currentPoint % width == 0)
{
_x = initX;
_y = ((int)currentPoint / width) * chessLength initY;
}
else
{
_x = chessLength;
}
tmpBox = new PictureBox();
tmpBox.Left = _x;
tmpBox.Top = _y;
tmpBox.Width = chessLength;
tmpBox.Height = chessLength;
map[(int)currentPoint / width, currentPoint % width] = tmpBox;
numMap[(int)currentPoint / width, currentPoint % width] = -1; //-1表示未遍历过
this.Controls.Add(tmpBox);
tmpBox = null;
currentPoint ;
}
}
//创建迷宫状态数据
private void CreateNumMap(int m,int n,int o)
{
List<int> directs = new List<int> { 0, 1, 2, 3 }; //存储未用的方向。0123分别表示上-右-下-左
int last=0;
switch (o)
{
case 1:
last = 4;
break;
case 2:
last = 8;
break;
case 4:
last = 1;
break;
case 8:
last = 2;
break;
}
numMap[m, n] = last;
//test-begin
string s = "";
for (int f = 0; f < height; f )
{
for (int g = 0; g < width; g ) s = numMap[f, g].ToString() ",";
s = "\r\n";
}
txt_str.Text = s;
//test-end
while (directs.Count > 0)
{
int x = m;
int y = n;
int d = rand.Next(directs.Count);
int t=0;
switch (directs[d])
{
case 0:
x--;
t = 8;
break;
case 1:
y ;
t = 4;
break;
case 2:
x ;
t = 2;
break;
case 3:
y--;
t = 1;
break;
}
directs.RemoveAt(d); //删除使用过的方向
if(x<height&&y<width&&x>=0&&y>=0&&numMap[x,y] == -1)//没有超出数组边界,格子未被遍历过,则为true
{
last = t ^ last; //异或操作
numMap[m, n] = last;
//test-begin
string ss = "";
for (int f = 0; f < height; f )
{
for (int g = 0; g < width; g ) ss = numMap[f, g].ToString() ",";
ss = "\r\n";
}
txt_str.Text = ss;
//test-end
CreateNumMap(x, y, t); //递归操作
}
}
}
//生成迷宫
private void CreateMap()
{
numMap[0, 0] = numMap[0, 0] ^ 8;//打开一个缺口,作为进入口。
numMap[height - 1, width - 1] = numMap[height - 1, width - 1] ^ 2;//打开一个缺口作为出去口。
for (int m = 0; m < height; m )
{
for (int n = 0; n < width; n )
{
int x=numMap[m, n];
map[m, n].Image = ImageList[x];
}
}
map[0, 0].Image = PathImageList[numMap[0, 0]]; //给第一格子换成橘黄色的背景
}
//寻路
private void Pathfinding(int x, int y)
{
if (x == height-1 && y == width-1)
{
for (int f = 0; f < height; f )
{
for (int g = 0; g < width; g )
{
if (path[f, g] != 0)
{
map[f,g].Image=PathImageList[numMap[f,g]];
}
}
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i )
{
int m = x;
int n = y;
int direct = 0;
switch (i)
{
case 0:
m --;
direct = 8;
break;
case 1:
n ;
direct = 4;
break;
case 2:
m ;
direct = 2;
break;
case 3:
n --;
direct = 1;
break;
}
if (m < height && n < width && m >= 0 && n >= 0 && (numMap[x, y] & direct) != 0 && path[m, n]==0)
{
path[x, y]= 1;
Pathfinding(m, n);
path[x, y] = 0;
}
}
}
}
相关软件
小贴士
感谢您为本站写下的评论,您的评论对其它用户来说具有重要的参考价值,所以请认真填写。
- 类似“顶”、“沙发”之类没有营养的文字,对勤劳贡献的楼主来说是令人沮丧的反馈信息。
- 相信您也不想看到一排文字/表情墙,所以请不要反馈意义不大的重复字符,也请尽量不要纯表情的回复。
- 提问之前请再仔细看一遍楼主的说明,或许是您遗漏了。
- 请勿到处挖坑绊人、招贴广告。既占空间让人厌烦,又没人会搭理,于人于己都无利。
关于好例子网
本站旨在为广大IT学习爱好者提供一个非营利性互相学习交流分享平台。本站所有资源都可以被免费获取学习研究。本站资源来自网友分享,对搜索内容的合法性不具有预见性、识别性、控制性,仅供学习研究,请务必在下载后24小时内给予删除,不得用于其他任何用途,否则后果自负。基于互联网的特殊性,平台无法对用户传输的作品、信息、内容的权属或合法性、安全性、合规性、真实性、科学性、完整权、有效性等进行实质审查;无论平台是否已进行审查,用户均应自行承担因其传输的作品、信息、内容而可能或已经产生的侵权或权属纠纷等法律责任。本站所有资源不代表本站的观点或立场,基于网友分享,根据中国法律《信息网络传播权保护条例》第二十二与二十三条之规定,若资源存在侵权或相关问题请联系本站客服人员,点此联系我们。关于更多版权及免责申明参见 版权及免责申明



网友评论
我要评论